Updated on: December 13, 2018
Contents
The Introduction
These procedures will certainly show you how to make use of a digital multimeter (DMM), a vital device that you can make use of to detect circuits, discover other people’s electronic designs, and also use Fluke 87 multimeter. For this reason the ‘multi’-‘meter’ or several dimension name.
One of the most fundamental things we measure are voltage and also current. A multimeter is likewise terrific for some basic peace of mind checks as well as troubleshooting. Is your circuit not functioning? Does the switch job? Place a meter on it! The multimeter is your very first protection when troubleshooting a system. In this tutorial we will cover measuring voltage, current, resistance and continuity.
Every fixer needs to recognize their way around a multimeter, which has simply north of a zillion uses for testing digital components and also circuits.
In this tutorial we’re mostly likely to reveal you just how to utilize a multimeter. This tutorial is primarily attended to for beginners that are beginning in electronics and have no concept just how to utilize a multimeter as well as exactly how it can be helpful. We’ll discover one of the most usual features on a multimeter and also exactly how to measure current, voltage, resistance and also just how to inspect continuity.
What is a multimeter as well as why do you require one?
A multimeter is a measurement tool definitely necessary in electronics. It incorporates three important attributes: a voltmeter, ohmeter, and ammeter, and in many cases continuity.
The tool permits you to understand what is taking place in your circuits. Whenever something in your circuit isn’t working, it will assist you troubleshooting. Right here’s some circumstances in electronics tasks that you’ll locate the multimeter beneficial:
- is the button turn on?
- is this cord conducting the electrical energy or is it damaged?
- just how much current is moving through this led?
- exactly how much power do you have left on your batteries?
What would multimeters measure?
Nearly all multimeters can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
A couple of multimeters have a continuity check, resulting in a loud beep if two points are electrically attached. This is handy if, as an example, you are building a circuit and also linking cables or soldering; the beep shows whatever is attached and nothing has actually come loose. You can additionally utilize it to make certain 2 things are not attached, to help prevent brief circuits.
Certain multimeters also have a diode check function. A diode resembles a one-way shutoff that only allows electricity circulation in one direction. The precise function of the diode check can vary from one type to another. If you’re collaborating with a diode and also can’t inform which method it enters the circuit, or if you’re uncertain the diode is functioning properly, the check attribute can be fairly helpful. If your DMM has a diode check feature, checked out the guidebook to figure out specifically how it functions.
Advanced models might have various other features, such as the capacity to measure as well as determine various other electrical parts, like transistors or capacitors. Since not all other multimeters have these functions, we will certainly not cover them in this tutorial. You can review your multimeter’s guidebook if you need to utilize these functions.
What Do Each Of the Symbols Mean?

There’s a lot taking place when you consider the selection knob, yet if you’re only mosting likely to be doing some standard stuff, you will not even make use of half of all the setups. All the same, here’s a run-through of what each sign suggests:
Direct Current Voltage (DCV):In some cases it will certainly be represented with a V– instead. This setup is made use of to measure straight current (DC) voltage in points like batteries.
Alternating Current Voltage (ACV): Sometimes it will be denoted with a V ~ instead. This setup is utilized to measure the voltage from alternating current sources, which is rather much anything that connects into an electrical outlet, in addition to the power coming from the electrical outlet itself.
Resistance (Ω): This gauges just how much resistance there is in the circuit. The reduced the number, the less complicated it is for the current to stream with, and also vice versa.
Continuity: Usually signified by a wave or diode symbol. This merely examines whether or not a circuit is complete by sending out a really percentage of current via the circuit as well as seeing if it makes it out the other end. Otherwise, then there’s something along the circuit that’s triggering an issue– discover it!
Straight Current Amperage (DCA): Similar to DCV, however rather than giving you a voltage reading, it will certainly inform you the amperage.
Direct Current Gain (hFE): This setting is to evaluate transistors and also their DC gain, yet it’s mostly ineffective, since most electricians and hobbyists will utilize the continuity check rather.
Your multimeter may additionally have a specialized setting for testing the amperage of AA, AAA, and also 9V batteries. This setup is usually signified with the battery icon.
Again, you probably will not even make use of fifty percent of the setups shown, so don’t get bewildered if you just recognize what a few of them do.
How to Utilize a Multimeter
For beginners, let’s discuss a few of the different parts of a multimeter. At the very basic degree you have the tool itself, together with 2 probes, which are the black and red wires that have plugs on one end and steel tips on the other.
The tool itself has a display screen on top, which gives you your readout, and also there’s a big selection knob that you can spin around to choose a certain setting. Each setting may also have various number values, which are there to measure various strengths of voltages, resistances, and also amps. So if you have your multimeter collection to 20 in the DCV area, it will measure voltages approximately 20 volts.
Your DMM will certainly also have two or three ports for plugging in the probes:
- the COM port mean “Common”, and the black probe will certainly always link into this port.
- the VΩmA port (sometimes denoted as mAVΩ) is simply a phrase for voltage, resistance, as well as current (in milliamps). This is where the red probe will certainly connect into if you’re measuring voltage, resistance, continuity, and also current less than 200mA.
- the 10ADC port (sometimes signified as simply 10A) is used whenever you’re measuring current that’s even more than 200mA. If you’re not exactly sure of the current draw, begin with this port. On the various other hand, you would certainly not utilize this port whatsoever if you’re measuring anything other than current.
Warning: Make sure that if you’re measuring anything with a current greater than 200mA, you plug the red probe into the 10A port, instead than the 200mA port. Otherwise you can blow the fuse that’s within the multimeters. Additionally, measuring anything over 10 amps can blow a fuse or destroy the multimeters also.
Your measurement tool could have entirely different ports for measuring amps, while the various other port is especially simply for voltage, resistance, and continuity, yet most cheaper multimeters will certainly share ports.
Anyway, let’s obtain begun really making use of a multimeter. We’ll be measuring the voltage of a AA battery, the current draw of a wall surface clock, and also the continuity of an easy wire as some examples to get you started as well as knowledgeable about making use of a multimeter.
Components of Multimeters
A multimeter has actually four components:
- Display: this particular is where the dimensions are shown
- Selection Knob: this selects what you intend to measure
- Ports: this is where you plug in the probes
- Probes: a multimeter includes 2 probes. Generally, one is red as well as the various other is black.
Ports
- “COM” or “–” port is where the black probe should be linked. The COM probe is traditionally black.
- 10A is utilized when measuring big currents, above 200mA.
- µAmA is made use of to measure current.
- VΩ permits you to measure voltage as well as resistance as well as examination continuity.
COM
COM represent common as well as is often linked to Ground or ‘-‘ of a circuit.The COM probe is traditionally black but there is no distinction between the red probe as well as black probe various other than color.
10A
10A is the unique port made use of when measuring big currents (above 200mA).
Selection Knob
The selection knob enables the individual to set the tool to read various points such as milliamps (mA) of current, voltage (V) and also resistance (Ω).
Probes
Two probes are linked into 2 of the ports on the front of the system. The probes have a banana kind connector on the end that connects into the multimeter. Any probe with a banana plug will deal with this meter. This enables different kinds of probes to be used.
Probe Types
There are various sorts of probes available. Right here are a few of our faves:
- Banana to Alligator Clips: These are fantastic cables for linking to huge cables or pins on a breadboard. Helpful for executing longer term tests where you don’t need to need to hold the probes in area while you control a circuit.
- Banana to IC Hook: IC hooks function well on smaller sized ICs and legs of ICs.
- Banana to Tweezers: Tweezers come in handy if you are needing to check SMD parts.
- Banana to Test Probes: If you ever before break a probe, they are cheap to replace!
Measuring Voltage

To begin, let’s measure voltage on a AA battery: Plug the black probe right into COM as well as the red probe right into mAVΩ. Establish to “2V” in the DC (straight current) range. Nearly all mobile electronic devices make use of direct current), not alternating current. Attach the black probe to the battery’s ground or ‘-‘ and also the red probe to power or ‘+’. Press the probes with a little pressure against the favorable and unfavorable terminals of the AA battery. If you’ve obtained a fresh battery, you must see around 1.5 V on the screen (this battery is brand-new, so its voltage is somewhat more than 1.5 V).
You may measure DC voltage or AC voltage. The V with a straight line indicates DC voltage. The V with the curly line implies AC voltage.
To measure voltage:
- Set the mode to V with a wavy line if you’re measuring AC voltage or to the V with a straight line if you’re measuring DC voltage.
- Make certain the red probe is linked to the port with a V next to it.
- Connect the red probe to the silver lining of your component, which is where the current is originating from.
- Attach the COM probe to the opposite side of your component.
- Review the value on the screen.
Tip: to measure voltage you have to connect your multimeter in parallel with the component you want to measure the voltage. Positioning the multimeter in parallel is putting each probe along the leads of the component you intend to measure the voltage.
Measuring a battery’s voltage
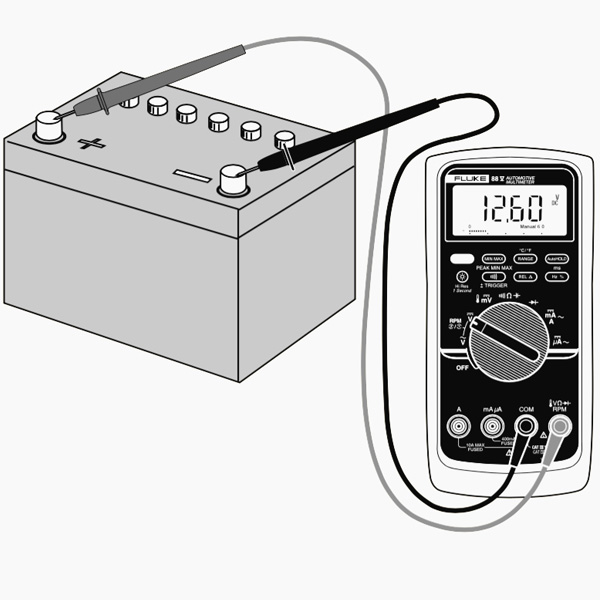
In this instance we’re going to measure the voltage of a 1.5 V battery. You recognize that you’ll have about 1.5 V. So, you must choose a variety with the selection knob that can read the 1.5 V. So you should choose 2V in the instance of this multimeter. If you obtain an autorange one, you don’t have to bother with the variety you need to choose.
Begin by turning on it, plugging the probes into their respective ports and afterwards setting the selection knob to the highest possible number worth in the DCV area, which in my case is 500 volts. If you do not recognize at the very least the voltage variety of things you’re measuring, it’s constantly an excellent concept to start with the highest possible worth initially as well as after that work your means down till you get a precise analysis.
In this case, we know the AA battery has a very reduced voltage, yet we’ll begin at 200 volts just for the purpose of instance. Next off, place the black probe on the unfavorable end of the battery as well as the red probe on the positive end. Have a look at the reading on the screen. Given that we have the multimeter set to a high 200 volts, it reveals “1.6” on the screen, meaning 1.6 volts.
However, I desire a more precise reading, so I’ll move the selection knob reduced to 20 volts. Below, you can see that we have an even more exact reading that hovers in between 1.60 and also 1.61 volts. If you were to ever establish the selection knob to a number worth reduced than the voltage of things you’re testing, the multimeter would certainly just check out “1”, signifying that it’s overwhelmed. So if I were to establish the handle to 200 millivolts (0.2 volts), the 1.6 volts of the AA battery is excessive for the multimeter to take care of at that setting.
In any instance, you could be asking why you would require to examine the voltage of something to begin with. Well, in this case with the AA battery, we’re examining to see if it has any kind of juice left. At 1.6 volts, that’s a fully-loaded battery. Nevertheless, if it were to read 1.2 volts, it’s close to being unusable.
In a much more useful circumstance, you might do this kind of measuring on an automobile battery to see if it could be dying or if the alternator (which is what bills the battery) is spoiling. An analysis between 12.4-12.7 volts indicates that the battery remains in excellent form. Anything reduced and that’s proof of a dying battery. In addition, start your car up as well as rev it up a bit. If the voltage doesn’t enhance to around 14 volts or so, then it’s likely that the generator is having problems.
Overload
What happens if you pick a voltage setup that is also low for the voltage you’re attempting to measure? Absolutely nothing bad. The meter will merely display a 1. This is the meter attempting to tell you that it is overloaded or out-of-range. Whatever you’re trying to check out is way too much for that specific setting. Try changing the multimeter knob to a the following highest setup.
Selection Knob
Exactly why does the meter knob reviewed 20V and not 10V? If you’re seeking to measure a voltage much less than 20V, you look to the 20V setup. This will certainly permit you to review from 2.00 to 19.99. The initial figure on many multimeters is just able to show a ‘1’ so the arrays are limited to 19.99 rather of 99.99. Thus the 20V max range as opposed to 99V max array.
Measuring Resistance

Connect the red probe right into the appropriate port and turn the selection knob to the resistance area. After that, link the probes to the resistor leads. The means you connect the leads doesn’t matter, the result is the exact same.
Normal resistors have color codes on them. If you don’t recognize what they indicate, that’s ok! There are lots of on the internet calculators that are simple to use. Nevertheless, if you ever discover yourself without net accessibility, a multimeter is very useful at measuring resistance.
Pick a random resistor and also set the multimeter to the 20kΩ setup. After that hold the probes versus the resistor legs with the same amount of pressure you when pressing a trick on a key-board.
The meter will certainly read one of three points, 0.00, 1, or the actual resistor worth.
In this instance, the meter reviews 0.97, meaning this resistor has a value of 970Ω, or regarding 1kΩ (remember you are in the 20kΩ or 20,000 Ohm setting so you require to move the decimal 3 areas to the right or 970 Ohms).
If the multimeter checks out 1 or presents OL, it’s overloaded. You will need to attempt a greater mode such as 200kΩ mode or 2MΩ (megaohm) mode. There is no damage if this take place, it simply implies the variety handle needs to be adjusted.
Should the multimeter reviews 0.00 or nearly no, after that you need to decrease the mode to 2kΩ or 200Ω.
Bear in mind that several resistors have a 5% resistance. This suggests that the shade codes might suggest 10,000 Ohms (10kΩ), however due to the fact that of inconsistencies in the manufacturing procedure a 10kΩ resistor could be as low as 9.5 kΩ or as high as 10.5 kΩ. Don’t fret, it’ll work just great as a pull-up or general resistor.
As a rule of thumb, it’s rare to see a resistor less than 1 Ohm. Bear in mind that measuring resistance is not best. Temperature level can affect the reviewing a great deal. Additionally, measuring resistance of a device while it is physically set up in a circuit can be extremely tricky. The bordering components on a motherboard can considerably impact the analysis.
The mockup usually looks like with a basic clock running of a AA battery. On the silver lining, the wire going from the battery to the clock is separated. We just put our 2 probes in between that break to finish the circuit once again (with the red probe linked to the source of power), only this time around our multimeter will certainly read out the amps that the clock is drawing, which in this case is around 0.08 mA.
While the majority of multimeters can also measure rotating current (AC), it’s not actually a great concept (specifically if its live power), because AC can be hazardous if you finish up making an error. If you need to see whether an outlet is functioning, utilize a non-contact tester instead.
To measure current you need to birth in mind that elements in collection share a current. So, you require to link your multimeter in collection with your circuit.
IDEA: to place the multimeter in collection, you need to place the red probe on the lead of a component and also the black probe on the next component lead. The multimeter acts as if it was a cable in your circuit. If you disconnect the multimeter, your circuit will not function.
Prior to measuring the current, be sure that you’ve plugged in the red probe in the best port, in this situation µAmA. In the example listed below, the exact same circuit of the previous example is used. The multimeter becomes part of the circuit.
Testing Continuity

If there is very reduced resistance between 2 factors, which is much less than a few ohms, the two points are electrically connected and also you’ll listen to a continuous audio. If the noise isn’t continual or if you don’t listen to any type of sound in any way, it suggests that what you’re testing has a defective connection or isn’t attached in any way.
WARNING: To examine continuity you must turn off the system. Switch off the power supply.
Touch both probes together and, as they are attached, you’ll listen to a continual sound.To test the continuity of a cord, you simply need to attach each probe to the cable tips.
Continuity is a terrific means to evaluate if two SMD pins are touching. If your eyes can not see it, the multimeter is typically a wonderful 2nd testing source. When a system is not functioning, continuity is one more thing to assist fix the system.
- Set your multimeter to the continuity setting making use of the selection knob.
- The readout on the display will immediately read “1”, which suggests that there isn’t any kind of continuity. This would be right because we have not attached the probes to anything yet.
- Next, ensure the circuit is unplugged and also has no power. After that connect one probe to one end of the cable as well as the various other probe to the various other end– no matter which probe takes place which end. If there is a complete circuit, your multimeter will either beep, show a “0”, or something aside from a “1”. If it still reveals a “1”, then there’s a trouble and also your circuit isn’t complete.
- You can likewise examine that the continuity function services your multimeter by touching both probes to each various other. This completes the circuit and your multimeter ought to let you understand that.
A continuity examination informs us whether two points are electrically connected: if something is continual, an electrical current can flow easily from one end to the other.
If there’s no continuity, it suggests there is a break someplace in the circuit. This could suggest anything from a blown fuse or poor solder joint to an improperly wired circuit.
Changing the Fuse
Among one of the most common errors with a brand-new multimeter is to measure current on a bread board by penetrating from VCC to GND. This will quickly short power to ground through the multimeter creating the bread board power supply to brown out. As the current rushes through the multimeter, the internal fuse will certainly warm up and afterwards stress out as 200mA streams via it. It will certainly occur in a split second and also with no genuine audible or physical indication that something is incorrect.
Bear in mind that measuring current is done in series (disturb the VCC line to the breadboard or microcontroller to measure current). If you try to measure the current with a blown fuse, you’ll most likely see that the meter reviews ‘0.00’ which the system doesn’t switch on like it ought to when you attach the multimeter. This is because the inner fuse is damaged and acts as a broken cable or open.
To alter the fuse, locate your helpful dandy mini screw vehicle driver, as well as start taking out screws. The components and also PCB traces inside the multimeter are designed to take different quantities of current. You will harm and perhaps destroy your multimeter if you unintentionally press 5A with the 200mA port.
There are times where you need to measure high current tools like a motor or home heating aspect. Do you see both locations to place the red probe on the front of the multimeter? 10A left wing as well as mAVΩ on the right? If you attempt to measure even more than 200mA on the mAVΩ port you run the danger of blowing the fuse. However if you make use of the 10A port to measure current, you run a much lower threat of blowing the fuse. The trade-off is sensitivity. As we spoke about above, by using the 10A port and also knob setting, you will just have the ability to review down to 0.01 A or 10mA. A lot of systems make use of more than 10mA so the 10A setup and port functions well sufficient. If you’re trying to measure very low power (micro or nano amps) the 200mA port with the 2mA, 200uA, or 20uA can be what you require.
Final thought
You’re now prepared to utilize your digital multimeter to begin measuring the globe around you. Really feel cost-free to start utilizing it to respond to lots of questions. A digital multimeter will certainly address lots of inquiries regarding electronics.
A multimeter is an important device in any type of electronic devices laboratory. In this guide, we’ve shown you How To Use a Multimeter. You’ve found out exactly how to measure voltage, current and also resistance, and just how to inspect continuity.
